Ammonium Ferric Sulphate: An In-Depth Product Description
Ammonium ferric sulphate, commonly referred to as ammonium iron(III) sulfate, is a chemical compound with the formula NH4Fe(SO4)2·12H2O. This compound is well-known for its distinctive properties and versatile applications across various industries, including water treatment, pharmaceuticals, and food processing. With its high solubility and stability, ammonium ferric sulphate serves as an essential ingredient in numerous chemical processes. This detailed product description will explore its properties, applications, benefits, and safety measures, providing valuable insights for anyone interested in ammonium ferric sulphate.
Chemical Properties
Composition and Structure
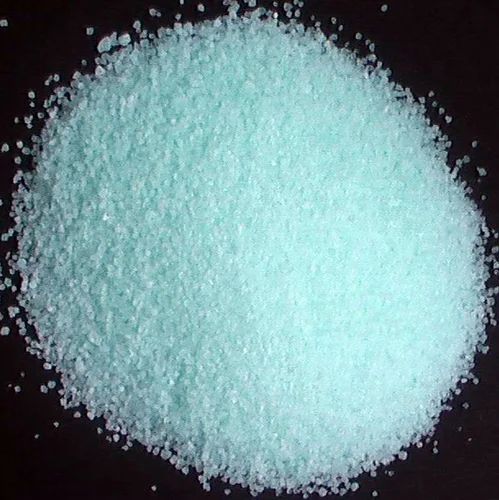
Ammonium ferric sulphate consists of ammonium ions (NH4+), ferric ions (Fe³+), and sulfate ions (SO4²−). The compound is typically found as a dodecahydrate, meaning it contains twelve molecules of water for every molecule of ammonium ferric sulphate, contributing to its crystalline structure and solubility.
Physical Characteristics
- Appearance: Light green to yellow crystalline solid
- Molecular Weight: Approximately 392.14 g/mol
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water
- Melting Point: Decomposes above 100 °C (212 °F)
- pH: Slightly acidic when dissolved in water
These properties make ammonium ferric sulphate a valuable compound for various applications across multiple sectors.
Applications of Ammonium Ferric Sulphate
1. Water Treatment
One of the primary uses of ammonium ferric sulphate is in water treatment processes. It serves as a coagulant, helping to remove impurities and suspended particles from water. By promoting the aggregation of particles, ammonium ferric sulphate effectively clarifies water, making it suitable for drinking and industrial use. Its ability to enhance flocculation makes it a preferred choice in municipal water treatment plants.
2. Pharmaceuticals
In the pharmaceutical industry, ammonium ferric sulphate is used as a source of iron in various formulations. It is beneficial for treating iron deficiency anemia, providing a readily absorbable form of iron. Additionally, it may be included in dietary supplements aimed at boosting iron levels in individuals, particularly pregnant women and those with increased iron requirements.
3. Food Processing
Ammonium ferric sulphate is often employed as a food additive. It acts as a firming agent and a color stabilizer in various food products. Its unique properties contribute to the preservation of color and texture, making it useful in the production of canned vegetables and fruit juices.
4. Analytical Chemistry
In laboratories, ammonium ferric sulphate is used as a reagent in analytical chemistry. It is involved in various chemical reactions, including the determination of phosphates and sulfates. Its role as a colorimetric reagent allows for the quantification of specific compounds, making it essential for accurate analytical results.
5. Dyeing and Tanning
Ammonium ferric sulphate is utilized in the dyeing and tanning industries. It acts as a mordant, helping to fix dyes onto fabrics and leather products. Its ability to enhance color retention and stability makes it a valuable ingredient in textile and leather production.
Advantages of Using Ammonium Ferric Sulphate
1. High Efficiency
Ammonium ferric sulphate is highly effective in its applications, particularly in water treatment and pharmaceuticals. Its ability to promote flocculation and coagulation ensures efficient removal of impurities from water, while its iron content provides a reliable source for dietary supplements.
2. Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to other coagulants and iron sources, ammonium ferric sulphate is relatively inexpensive. This cost-effectiveness makes it an attractive option for industries seeking reliable solutions without significant financial investment.
3. Stability
Ammonium ferric sulphate is stable under normal storage conditions, ensuring its reliability in various applications. Its solubility in water allows for easy incorporation into formulations and processes.
4. Versatility
The diverse applications of ammonium ferric sulphate make it a highly versatile compound. Its effectiveness in water treatment, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and analytical chemistry demonstrates its adaptability across multiple sectors.
How to Use Ammonium Ferric Sulphate
1. In Water Treatment
When using ammonium ferric sulphate for water treatment:
- Dosage: Determine the appropriate dosage based on water quality and treatment goals. Typically, a range of 10-100 mg/L is effective for coagulation.
- Mixing: Dissolve the compound in water before adding it to the treatment process to ensure even distribution.
- Monitoring: Regularly monitor water quality to assess the effectiveness of treatment and adjust dosage as necessary.
2. In Pharmaceuticals
For pharmaceutical applications:
- Formulation: Incorporate ammonium ferric sulphate into supplements or medications following established guidelines for iron supplementation.
- Quality Control: Regularly test for purity and efficacy to ensure product standards are met.
3. In Food Processing
In food production:
- Compliance: Adhere to food safety regulations regarding the use of ammonium ferric sulphate as a food additive.
- Mixing: Ensure even distribution in food products to achieve consistent texture and color stabilization.
4. In Analytical Chemistry
In laboratory settings:
- Preparation: Dissolve ammonium ferric sulphate in the appropriate solvent as required by the analysis.
- Protocol Adherence: Follow established laboratory methods for accurate and reliable results.
Safety and Handling
1. Toxicity
Ammonium ferric sulphate is generally considered safe when handled properly. However, it can cause irritation to the skin, eyes, and respiratory system. It is important to take precautions to avoid exposure.
2. Protective Measures
When working with ammonium ferric sulphate, it is crucial to:
- Wear Protective Gear: Use gloves, goggles, and appropriate protective clothing to minimize exposure risks.
- Ensure Ventilation: Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling dust or fumes.
3. Storage
Store ammonium ferric sulphate in a cool, dry place away from incompatible substances. Ensure that containers are tightly sealed to prevent moisture absorption, which can lead to degradation.
Conclusion
Ammonium ferric sulphate is a versatile and essential compound utilized across various industries, including water treatment, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and analytical chemistry. Its unique properties, such as high efficiency and stability, make it an invaluable resource for professionals and manufacturers.
When purchasing ammonium ferric sulphate, choose reputable suppliers that provide high-quality products and detailed safety data sheets. Understanding its applications, benefits, and safety measures will help you maximize the potential of this remarkable compound in your projects.
Whether you’re a water treatment professional, a pharmacist, or a food manufacturer, ammonium ferric sulphate can meet your needs. Embrace the advantages of this compound and unlock new possibilities in your field!




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.